Introduction
Electric cooler boxes have revolutionized the way we keep perishables cool during road trips, camping adventures, and other outdoor activities. Unlike traditional coolers that rely on ice, electric cool boxes employ advanced technologies to maintain a consistent and adjustable temperature.
In this article, we will delve into the inner workings of electric cooler boxes, exploring the two primary cooling technologies, their components, and how they efficiently regulate temperatures on the go.
In this Article
1. Thermoelectric Technology
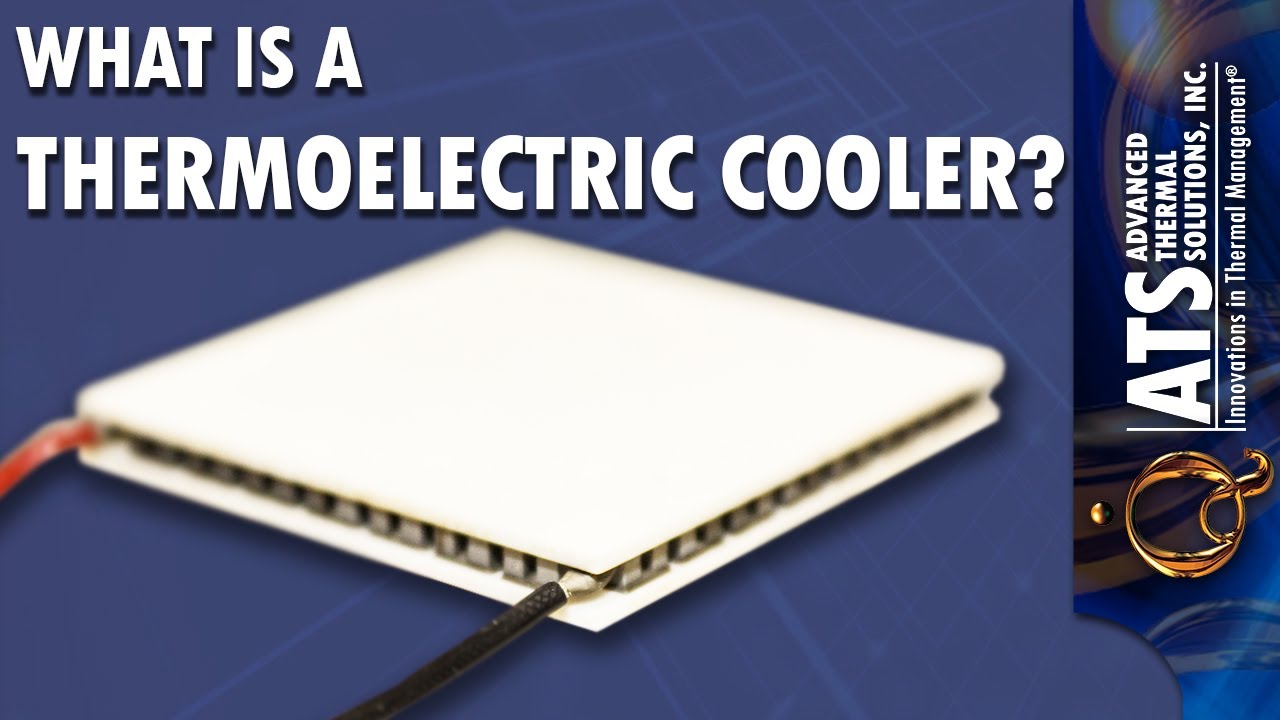
One of the common technologies employed in electric cooler boxes is thermoelectric cooling. This method relies on the Peltier effect, a phenomenon in which an electric current is passed through two different conductors, creating a heat differential. Here’s how it works:
- Peltier Module: The heart of a thermoelectric cooler is the Peltier module, a small semiconductor device comprising two plates of different materials. When an electric current passes through the module, it causes one side to absorb heat while the other releases it.
- Heat Transfer: The absorbed heat is transferred from the interior of the cooler to the exterior, allowing the contents inside to remain cool. The expelled heat is released into the surrounding environment.
- Temperature Control: Electric cooler boxes using thermoelectric technology often come with a control unit that allows users to adjust the temperature. While thermoelectric coolers are generally not as powerful as compressor-based models, they are energy-efficient and suitable for moderate cooling needs.
2. Compressor-Based Technology
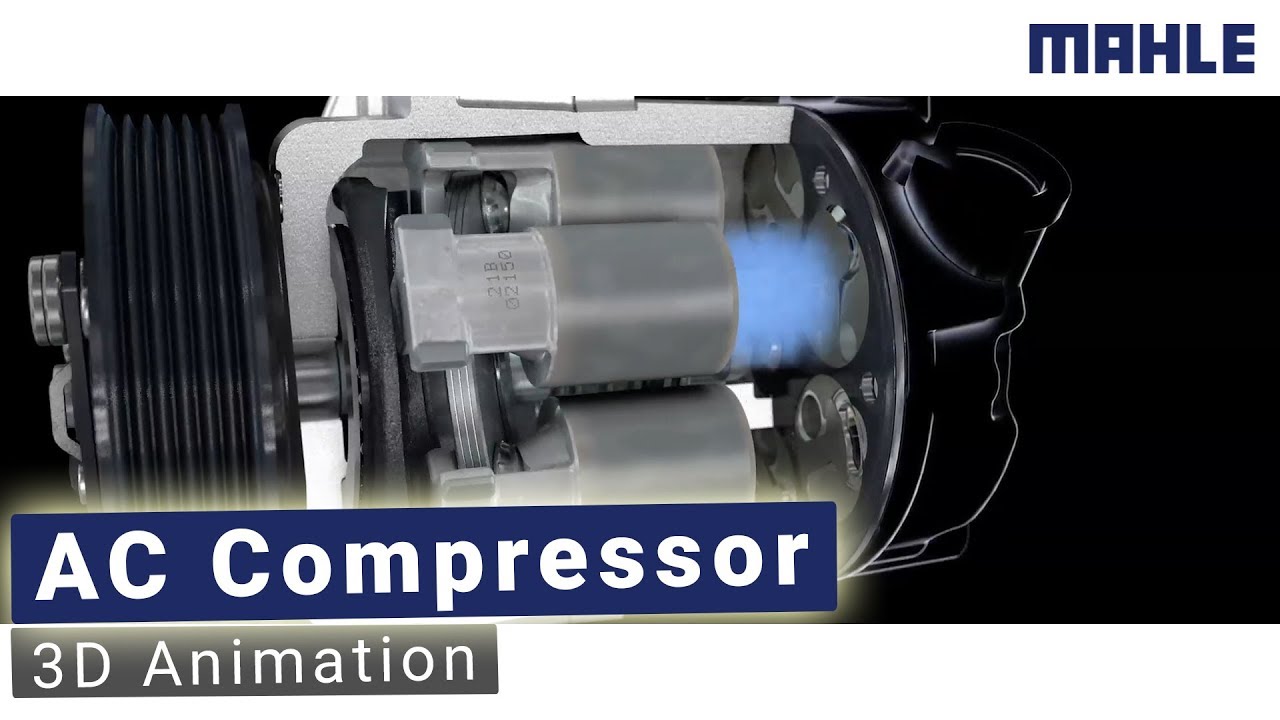
Compressor-based electric cooler boxes are more akin to traditional refrigerators, utilizing a compressor and refrigerant to achieve lower temperatures. Here’s a breakdown of how this technology operates:
- Compressor System: The heart of a compressor-based cooler is, unsurprisingly, the compressor. This component circulates a refrigerant (commonly a gas like R134a) through a closed system.
- Compression and Expansion: The refrigerant is compressed into a high-pressure, high-temperature gas by the compressor. This hot gas then passes through a condenser coil on the outside of the cooler, dissipating heat and turning into a liquid.
- Evaporation and Cooling: The liquid refrigerant is then allowed to expand through an expansion valve, causing it to evaporate and absorb heat from the interior of the cooler. This process cools the contents inside, and the cycle repeats.
- Temperature Regulation: Compressor-based coolers offer more precise temperature control and can achieve lower temperatures than thermoelectric models. They are suitable for situations where more powerful cooling is required.
Considerations for Purchasing an Electric Cool Box
When buying an electric cool box, there are several important factors to consider to ensure that the product meets your specific needs and preferences. Here’s a comprehensive list of factors to consider:
- Cooling Technology: Decide between thermoelectric and compressor-based cooling technologies. Thermoelectric coolers are generally more energy-efficient but may have limitations in achieving very low temperatures. Compressor-based coolers are more powerful and offer better temperature control but may consume more energy.
- Capacity: Consider the size of the electric cool box based on your intended use. Larger capacities are suitable for extended trips or when you need to store items for a group, while smaller capacities are more portable.
- Power Source: Check the power source compatibility. Most electric cool boxes operate on 12-volt DC power for use in cars, but some models can also switch to 110-240V AC power for use at home or other locations.
- Temperature Control: Look for models with adjustable temperature controls. This feature allows you to set the desired level of cooling, making it suitable for different types of items.
- Energy Efficiency: Evaluate the energy efficiency of the cooler, especially if you plan to use it for extended periods without running the car engine. Energy-efficient models help preserve your car’s battery life.
- Portability: Consider the design and portability of the cooler. Look for models with sturdy handles, a lightweight build, and compact dimensions for easy transportation.
- Construction and Durability: Check the build quality and materials used in the construction of the cooler. Durable materials and reinforced corners enhance the longevity of the product, especially if you plan to use it in outdoor settings.
- Noise Level: If noise is a concern, consider the noise level of the cooler. Thermoelectric coolers are generally quieter than compressor-based models, but advancements have been made in reducing noise in both types.
- Additional Features: Explore extra features such as USB ports for charging devices, LED lighting, dual-zone temperature settings, and the ability to switch between cooling and heating modes for added versatility.
- Brand and Reviews: Research and consider reputable brands known for producing reliable electric cool boxes. Read user reviews to gain insights into real-world experiences and satisfaction with specific models.
- Price: Establish a budget and compare prices across different models. Keep in mind that while upfront costs are essential, the long-term value and performance of the cooler should also be considered.
- Warranty and Customer Support: Check the warranty provided by the manufacturer. A longer warranty period can be an indication of the manufacturer’s confidence in the product. Additionally, assess the availability and responsiveness of customer support.
By carefully considering these factors, you can make an informed decision and choose an electric cool box that aligns with your requirements and provides a reliable cooling solution for your on-the-go needs.
FAQ’s (Frequently Asked Questions)
Conclusion
Electric cooler boxes have come a long way from relying solely on ice to keep items cool. Whether using thermoelectric or compressor-based technology, these portable coolers provide a convenient and efficient way to maintain low temperatures on the go.
Understanding the inner workings of these devices allows users to make informed choices based on their specific needs, ensuring that their outdoor adventures are accompanied by reliably cooled refreshments and perishables. As technology continues to advance, we can expect even more innovations in the field of portable cooling solutions, enhancing our outdoor experiences further.